This is a case is a 13-year-old female spayed domestic short haired cat with history of hematuria (blood in the urine).
Findings
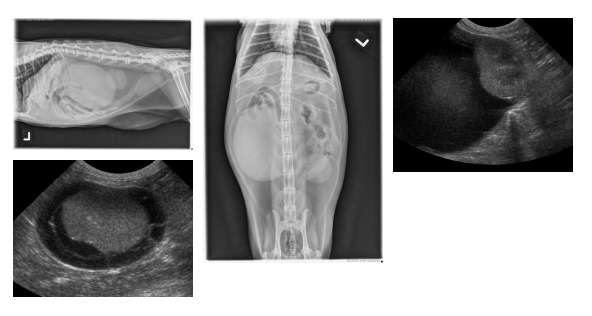
The right kidney is markedly enlarged, with a rounded shape. It is distorting the abdominal wall on the v/d projection and displacing the ascending and transverse colon medially and ventrally. The left kidney also has an abnormal shape, with reduced length and increased width.
There is also spondylosis deformans at the L5-6 intervertebral disc space, which is an incidental finding.
On ultrasound images, both kidneys were surrounded by large cystic structures filled with echogenic fluid. There are fine septae visible in the pseudocyst surrounding the left kidney. Drainage of both collections of fluid were clear and colorless except for the last 15 ml from the right kidney, which was hemorrhagic. Both kidneys were small and irregular with poor corticomedullary distinction.
Differential Diagnosis
Diagnosis
Bilateral perinephric pseudocysts and chronic renal disease.
Discussion
Perinephric pseudocysts are associated with chronic renal disease, but are often asymptomatic. The association between the pseudocysts and this cat’s hematuria is unclear. The hematuria may have been due to pressure from the pseudocysts, or idiopathic in nature.
Source: veterinaryradiology.net / Allison Zwingenberger
Findings
The right kidney is markedly enlarged, with a rounded shape. It is distorting the abdominal wall on the v/d projection and displacing the ascending and transverse colon medially and ventrally. The left kidney also has an abnormal shape, with reduced length and increased width.
There is also spondylosis deformans at the L5-6 intervertebral disc space, which is an incidental finding.
On ultrasound images, both kidneys were surrounded by large cystic structures filled with echogenic fluid. There are fine septae visible in the pseudocyst surrounding the left kidney. Drainage of both collections of fluid were clear and colorless except for the last 15 ml from the right kidney, which was hemorrhagic. Both kidneys were small and irregular with poor corticomedullary distinction.
Differential Diagnosis
- Perinephric pseudocysts
- Hydronephrosis
- Chronic renal disease
- Subcapsular hematoma
- Lymphosarcoma
Diagnosis
Bilateral perinephric pseudocysts and chronic renal disease.
Discussion
Perinephric pseudocysts are associated with chronic renal disease, but are often asymptomatic. The association between the pseudocysts and this cat’s hematuria is unclear. The hematuria may have been due to pressure from the pseudocysts, or idiopathic in nature.
Source: veterinaryradiology.net / Allison Zwingenberger

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
